There is no doubt that a presentation with relevant pictures is more effective than just a plain text presentation. Although pictures enhance the look of your presentation, they can also phenomenally increase the size of your presentation file. PowerPoint 2010 for Windows is better in that respect compared to previous versions because it does some compression even if you may not be aware. Even better, there is an option to make the compression even more effective.
This is the Compress Pictures feature. This feature offers an image compression utility that reduces the size of all inserted pictures in the presentation in a single step. It does so by reducing the picture resolution to the amount needed for the type of output you specify (E-mail, Screen, or Print). Picture resolution is measured in PowerPoint in pixels per inch, or ppi. This roughly translates to dots per inch (dpi) on a printout. A computer screen shows 96 pixels per inch, so you do not need higher resolution than that if you are only showing your presentation on-screen. However, if you are distributing the presentation in other forms, a higher resolution might be appropriate.
To reduce the resolution and compress images, follow these steps:
- Open the presentation, navigate to any slide that contains a picture and select it. This brings up Picture Tools Format contextual tab on the Ribbon as shown in Figure 1 (highlighted in red).
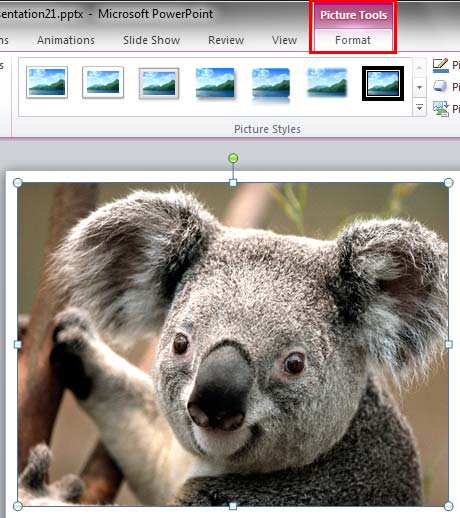
Figure 1: Picture Tools Format tab Note: The
Picture Tools Format tab is a
Contextual tab. Contextual tabs are special tabs in the
Ribbon that are not visible all the time. They make an appearance only when you are working with a particular slide object which can be edited using the options within these tabs.
- Within the Picture Tools Format tab, click the Compress Pictures button, as shown highlighted in red within Figure 2.
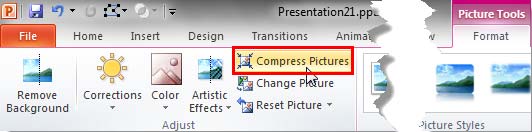
Figure 2: Compress Pictures button - Doing so opens the Compress Pictures dialog box, as you can see in Figure 3.
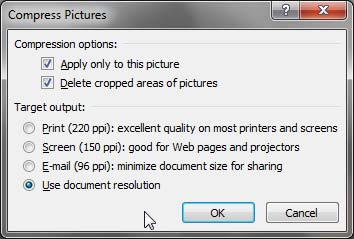
Figure 3: Compress Pictures dialog box - The Compress Pictures dialog box is divided into two sections: Compression options and Target output. Both these sections comprise some options which are explained below:
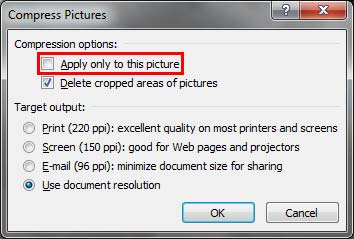
Figure 4: Apply only to this picture check-box deselected Apply only to this picture
- This check-box, when selected enables you to compress just the selected picture. If you want to compress all the pictures in the presentation make sure you deselect this check-box, as you can see highlighted in red within Figure 4, below.
Delete cropped areas of pictures
- If you applied cropping to the pictures and you want to delete the cropped-out areas of pictures to save additional space, select the Delete cropped areas of pictures check-box (see Figure 4, above).
Print (220 ppi)
- Select this radio button if you are printing the presentation on paper; it keeps the photos at a resolution where they will look crisp on a printout.
Screen (150 ppi)
- Choosing this radio button will enable compression for Screen resolution to display the presentation using a projector or distributing via the Internet. Some projectors have a higher resolution than a monitor.
E-mail (96 ppi)
- Select this radio button if you are e-mailing the presentation to others, because this lower setting results in a smaller file that will transmit more easily via e-mail.
Note: Some e-mail servers have limits on the file sizes they accept, so keeping the PowerPoint file as small as possible when distributing via e-mail is a good idea. If you send someone an e-mail with a large file attached to it, the server may reject the message, but you might not get an error message back from the server at all, or you might not get one for several days.
Use Document Resolution
- Select this radio button to select the default output target for picture resolution. You can find default picture resolution within the PowerPoint Options dialog box. Explore our Set Document Resolution in PowerPoint 2010 tutorial to learn more.
- Choose the options based on your requirement, and click the OK button to apply the changes.
- Make sure you save your presentation.







